AI agents are everywhere. From enterprise platforms to startup demos, the term “Agentic AI” is being used to describe everything from chatbots to workflow automations. But here’s the problem: not all agents are created equal and calling them such can mislead buyers, stall innovation, and erode trust.
As Heather Hershey, Research Director at IDC, defines it, “Agentic AI is an autonomous artificial intelligence system that can independently plan, reason, make decisions, and execute multi-step tasks to achieve specific goals with minimal human intervention, incorporating persistent memory and real-time adaptability.”
That’s a high bar, and most tools labeled agents today don’t come close.
From Buzzword to Barrier: The Rise of Agent-Washing
AI agents exist on a spectrum of maturity. Some surface information and recommend next actions. Others aspire to Agent-to-Agent (A2A) interoperability, where systems collaborate across organizations without human mediation. But many so-called “agents” are dressed-up LLM workflows or glorified chatbots.
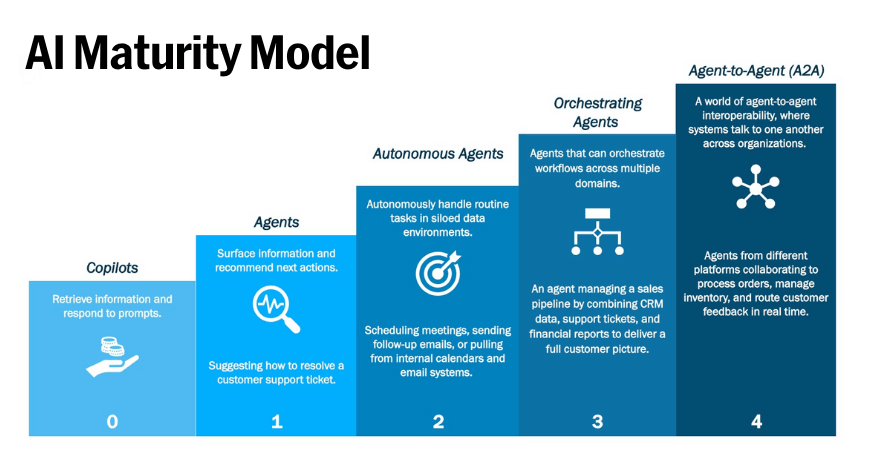
This maturity model is based on insights from Jeremy Kahn’s Eye on AI newsletter, published by Fortune on September 11, 2025.
What do we call it when a product is mislabeled as agentic? Agent- washing.
As Forbes puts it, “Agent washing may help companies ride the current hype cycle, but it comes at a cost. It confuses users, disappoints customers, and gums up the process of adopting tools that are genuinely transformative.”1
What Is Agent-Washing?
Agent-washing is the practice of branding basic AI workflows, scripted automations, or chat interfaces as “AI agents” without delivering the core capabilities that define true agentic intelligence. It’s like calling a calculator a financial advisor.
According to Gartner, “Most agentic AI projects right now are early-stage experiments or proof of concepts that are mostly driven by hype and are often misapplied.” They predict that over 40% of agentic AI projects will be canceled by 2027 due to unrealistic expectations and poor implementation.2
Why Agent-Washing Hurts Everyone
Agent-washing doesn’t just dilute the term ‘Agent’ it actively harms innovation by:
- Stalling adoption of truly transformative tools
- Blinding organizations to the real cost and complexity of deploying AI agents at scale
- Creating confusion in the market, making it harder to evaluate solutions
If we want to build a future powered by intelligent tools, we need clarity. As Forbes states, “We don’t necessarily need a rigid standard, but we do need clearer expectations about what these systems are supposed to do, how autonomously they operate, and how reliably they perform.”3 Heather Hershey, Research Director at IDC, adds that “I’ve seen many ‘agentic AI’ products in the past twelve months that, upon further investigation, were AI co-pilots or LLM wrappers on conventional machine learning. There was no ‘agent’ in the ’agentic AI’. Buyers will need to arm themselves with the knowledge of what agentic AI is and what it is not in order to avoid overpaying for features that cannot perform as promised.”
What Makes AI Agents Truly Agentic?
To separate hype from reality, we need to understand what defines a true AI Agent. Here are the four core principles of Agentic AI:
- Purposeful Action: Agents must understand and work toward specific goals, not just respond to prompts.4
- Autonomous Decision-Making: They should decide what to do next without constant human input. Think of them like employees who know when to act and when to ask for help.4
- Resource Awareness: True agents know what tools they have access to (APIs, databases, services) and use them effectively.5
- Task Completion Tracking: They monitor progress, know when a goal is achieved, and adapt if it isn’t.6
- Iteration and Reiteration: Unlike traditional, one-shot AI models, an agentic system is defined by its ability to engage in a continuous, multi-step process to achieve its goals. This is how it’s able to build and refine workflows and adapt to the needs of specific users. (IDC Research Director, Heather Hershey)
- Probabilistic and Deterministic: As opposed to one versus the other. Agentic AI is a complex hybrid AI system that strategically uses the strengths of both probabilistic and deterministic AI to achieve a goal. The probabilistic components handle ambiguity and adapt to change, while the deterministic components provide the necessary control, accuracy, and reliability. (IDC Research Director, Heather Hershey)
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Agentic Capabilities
As AI agents increase in maturity, they:
- Retain memory and context learning from past interactions and improving over time.
- Integrate with external tools such as updating CRMs, sending messages, logging actions.
- Build structured workflows using flow engineering to plan, execute, and verify complex tasks.
- Enable adaptive user experiences involving humans at critical decision points.
If your “agent” performs the same way every time, regardless of context or feedback, it’s not truly agentic.
Why Clarity Is the Key to Progress
Agentic AI has the potential to revolutionize how we work. But that potential is wasted if we chase buzzwords instead of solving real problems.
Be on the lookout for buzzwords that contribute to agent-washing such as:
- “AI-powered ChatBot”: This is often just a conversational interface with no ability to take autonomous action or make decisions.
- “Intelligent Virtual Assistant”: While this may sound agentic, it often lacks goal-oriented planning or tool use beyond scripted responses.
- “AI Copilot”: A popular term that may imply autonomy but often refers to assistive tools that still rely heavily on human direction.
- “Conversational AI”: It’s great if the AI understands natural language, but without goal pursuit or decision-making, it should not be considered an agent.7
As Yoav Shoham puts it, “We need clearer expectations… about what these systems are supposed to do, how autonomously they operate, and how reliably they perform.”1
Agent-washing is more than a marketing misstep; it’s a barrier to progress. By understanding what true agentic AI looks like, businesses can make smarter investments, avoid costly failures, and unlock real value.
To download PROS Agentic AI Buyer’s Guide, click here.
Let’s stop chasing hype. Let’s start investing in intelligent systems that actually deliver value. To learn more about PROS AI agents visit this webpage.
Sources
1What Is AI Agent Washing, And Why Is It Everywhere?, Forbes
2Gartner Predicts Over 40% of Agentic AI Projects Will Be Canceled by End of 2027
3Why More AI Features Aren’t Always Better, Forbes
4A Practical Guide to AI Agents: Key agentic AI concepts, use cases and considerations to drive ROI, Snowflake
5What is an AI Agent?, McKinsey
6Agentic AI 101: Everything You Ever Wanted To Know About AI Agents But Never Dared Ask, Mindset
7What Is AI Agent Washing And Why Is It A Risk To Businesses?, Forbes
Frequently Asked Questions
Agentic AI refers to autonomous systems that plan, reason, and act towards goals with minimal human input.
The mislabeling of basic AI tools as “agents” without true agentic capabilities.
Download PROS Agentic Buyer’s Guide, learn the core traits of agentic AI and demand transparency from vendors.
It helps avoid hype-driven investments and ensures scalable AI success.

